The Windows Command Prompt (CMD) has been an essential tool for IT professionals, developers, and power users for decades. With just a few keystrokes, you can test network connectivity, analyze system performance, manage users, or troubleshoot common issues — all without opening a single graphical window.
In this article, we will explore the most commonly used CMD commands, along with practical examples such as ping, tasklist, tracert, and nslookup. These commands are not only useful for day-to-day troubleshooting but also form the foundation for deeper system administration and automation tasks.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ping [ip/domain] | Test network connectivity |
| tracert [ip/domain] | Packet route (hop tracing) |
| nslookup [domain] | DNS resolution |
| ipconfig | IP information |
| ipconfig /all | Detailed network information |
| ipconfig /renew | Renew IP address |
| ipconfig /release | Release IP address |
| arp -a | ARP table |
| getmac | MAC address |
| netstat -ano | Ports, connections, and PID info |
| netstat -rn | Routing table |
| netstat -s | Protocol statistics |
| pathping [ip/domain] | Packet loss + latency test |
| telnet [ip] [port] | Port connectivity test |
| netsh wlan show profile | Saved Wi-Fi profiles |
| netsh wlan show profile name=”SSID” key=clear | Display Wi-Fi password |
| route print | Routing table |
| ftp [ip] | FTP connection |
| hostname | Computer name |
| whoami | Current logged-in user |
| taskmgr | Task Manager |
| msconfig | System configuration |
| services.msc | Services management |
| eventvwr.msc | Event viewer (logs) |
| gpedit.msc | Group Policy Editor |
| regedit | Registry Editor |
| compmgmt.msc | Computer Management |
| diskmgmt.msc | Disk Management |
| devmgmt.msc | Device Manager |
| cleanmgr | Disk cleanup |
| dxdiag | DirectX information |
| verifier | Driver verification |
| driverquery | List installed drivers |
| sfc /scannow | System file repair |
| chkdsk /f | Fix disk errors |
| systeminfo | System information (OS, patch level) |
| wmic product get name | List installed programs |
| wmic os get caption | Windows version |
| echo %username% | Display username |
| echo %computername% | Display computer name |
| net user | List user accounts |
| net user [username] [password] /add | Add new user |
| net localgroup administrators [username] /add | Grant admin rights |
| gpupdate /force | Refresh group policies |
| shutdown -s -t 30 | Shutdown in 30 seconds |
| shutdown -r -t 0 | Restart immediately |
| shutdown -l | Log off user |
| shutdown -i | Remote shutdown dialog |
| logoff | Log off session |
| cls | Clear console screen |
Example: ping <code>google.com
The ping command is one of the most commonly used CMD commands. It is used to test the connectivity between your computer and another host (such as a website or IP address).
In the example:
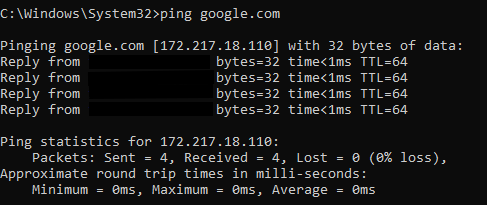
- The command sends 4 ICMP packets (by default) to
google.com. - The replies show:
- Reply from [IP address] → The destination is reachable.
- bytes=32 → Packet size (32 bytes).
- time<1ms → Response time (latency), here less than 1 millisecond.
- TTL=64 → Time to Live, indicating how many hops (routers) the packet can still pass through.
At the end, statistics are shown:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 → No packet loss, the connection is stable.
- Round Trip Times (Minimum, Maximum, Average) → Shows network speed and latency consistency.
In this case, the connection to Google is successful, with 0% packet loss and extremely low latency.
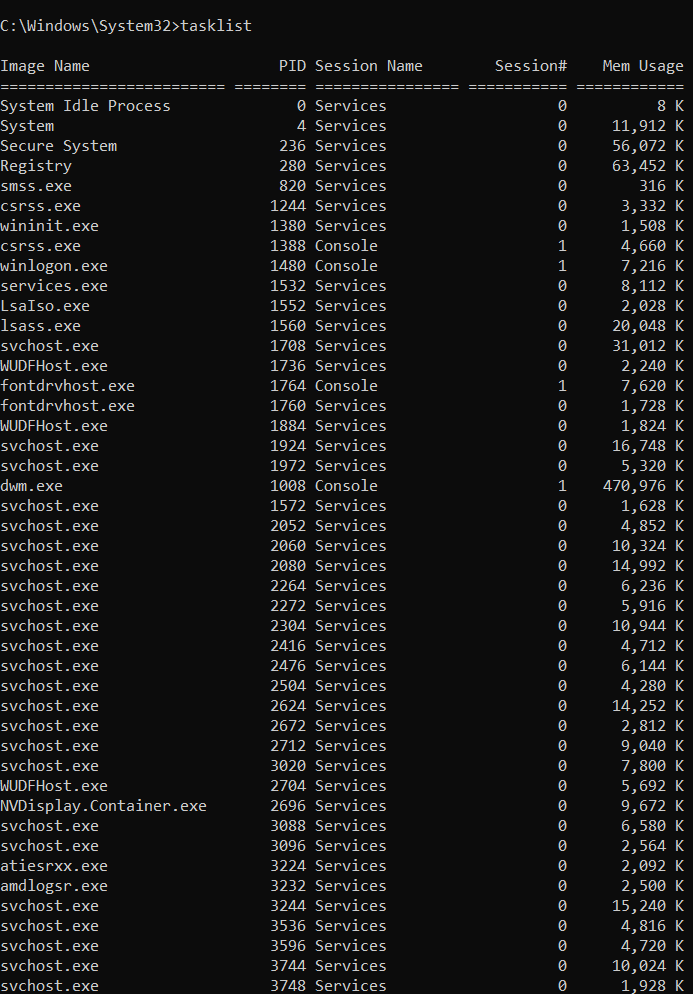
Example: tasklist
The tasklist command displays all currently running processes on a Windows system. It is very useful for monitoring system activity, troubleshooting, and identifying resource usage.
In the example above:
- Image Name → The name of the running process (e.g.,
svchost.exe,dwm.exe). - PID (Process ID) → A unique identifier assigned to each running process.
- Session Name / Session# → Indicates whether the process is running under the system services or a user session.
- Mem Usage → Shows the amount of memory (RAM) the process is currently using.
Why use tasklist?
- To check which applications or background services are running.
- To find memory-hungry processes that may slow down the system.
- To get the PID number, which can be used later with commands like
taskkillto end a process.
This makes tasklist a powerful tool for system administrators and developers who need quick insights into what is happening on the machine.
Example: tracert google.com
The tracert (Trace Route) command is used to determine the path that packets take to reach a destination (such as a website or server). It shows each “hop” the packet passes through along the way.
In the example above:
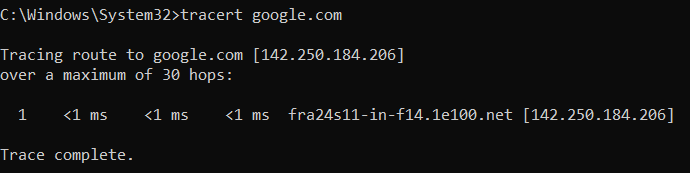
- The destination IP address is 142.250.184.206.
- The trace shows that the packets reached the target in just 1 hop with a response time of <1ms.
- The hostname fra24s11-in-f14.1e100.net indicates that the server is located in Google’s infrastructure (Frankfurt, Germany in this case).
Why use tracert?
- To identify network routing paths.
- To troubleshoot slow connections by checking where latency occurs.
- To see if a connection problem happens on your local network, your ISP, or beyond.
In this case, the connection to Google completed successfully with almost no delay.
Example: nslookup google.com
The nslookup (Name Server Lookup) command is used to query DNS servers to obtain the IP address of a domain name. It is very useful for troubleshooting DNS-related issues.
In the example above:
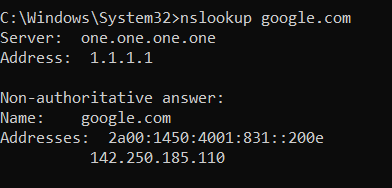
- The DNS server used is 1.1.1.1 (Cloudflare DNS).
- The command resolved the domain google.com to the following IP addresses:
- IPv6:
2a00:1450:4001:831::200e - IPv4:
142.250.185.110
- IPv6:
Why use nslookup?
- To check if a domain name resolves correctly to an IP address.
- To verify DNS server responses.
- To troubleshoot network connectivity problems related to DNS.
In this case, google.com correctly resolves to both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, confirming that the DNS resolution works as expected.
Learn more about our services here.
Contact us today to keep your ERP running at peak performance and reliability.here.









